Other parts of this series:
Insurers will need to master a new set of technologies as they begin to move beyond digital transformation to offer customers personalised on-demand insurance products and services in a post-digital world. DARQ technologies will change how products and services are created, served up and serviced, but will also offer significant benefits to the organisation and its workforce.
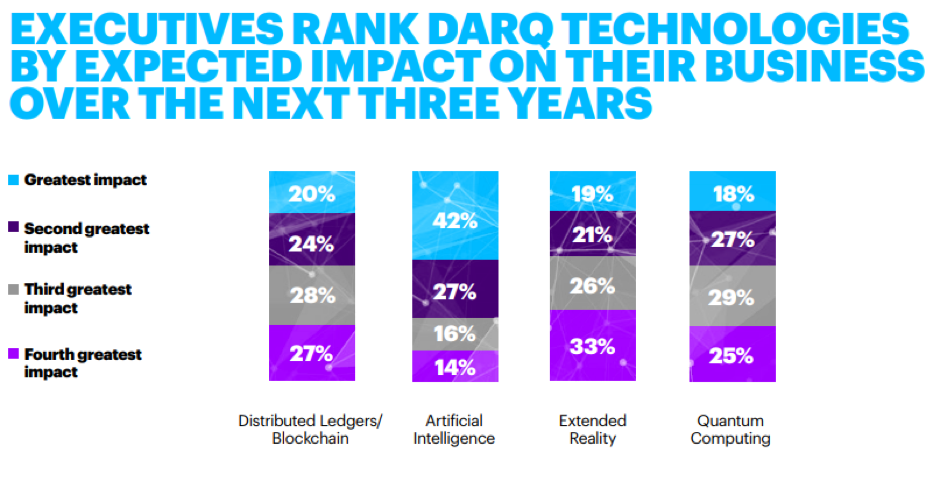
DARQ technologies comprise distributed ledger technology (DLT), artificial intelligence (AI), extended reality (XR) and quantum computing. Insurers are already getting their hands dirty—93 percent of insurers are already experimenting with one or more DARQ technologies, expecting them to be key differentiators.
93 percent of insurers are already experimenting with one or more DARQ technologies—that’s distributed ledger technology, AI, XR and quantum computing.
With a focus on talent and organisation, I am keen to understand how these technologies will impact or add value to the organisation and the workforce.
- AI already plays a critical role in optimizing processes and influencing strategic decision-making. Increasingly, it will also augment human outputs.
- Extended reality (XR)—immersive technologies like augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR)—create entirely new ways for people to experience and engage with the world around them. XR could be used to walk customers though product offerings or processes, but also to train employees or facilitate engagement between insurance representatives and customers.
- Distributed ledgers will expand networks by eliminating the need for trusted third parties.
Quantum technology—the least mature of the four technologies—could offer game-changing ways to approach and solve the hardest computational problems, such as running more sophisticated actuarial simulations for more real-time and precise pricing and risk pooling.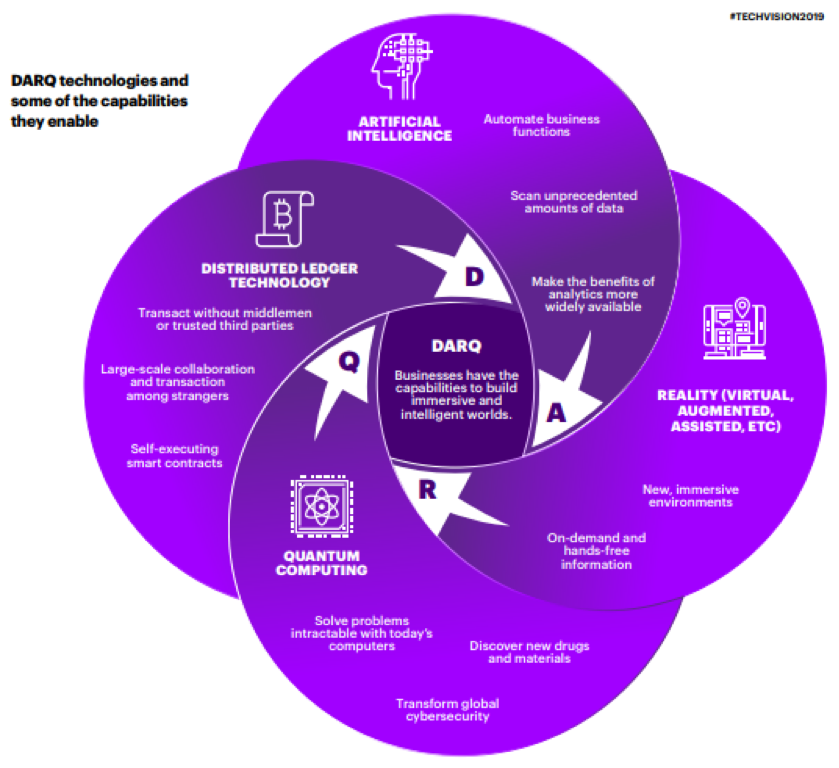
There are already a number of examples of how DARQ can improve efficiencies and automate previously time-consuming processes, freeing up workers to do higher value work.
DARQ at work
Sompo Japan Nipponkoa Insurance in Japan plans to use AI to recreate vehicle collisions from GPS, dashcam and historical accident data to shorten the gap between an auto accident and an insurance payout from about two months to two weeks or less.
AXA XL, meanwhile, is piloting AI and natural language processing software to help populate and process information on commercial business properties in an effort to free underwriters from a tedious, manual chore.
DARQ can improve efficiencies and automate previously time-consuming processes, freeing up workers to do higher value work.
Driving the post-digital future
DARQ will enable the post-digital era of business and technology, and insurers looking to lead in that era must start now. The insurance companies that recognise the opportunity—and begin to explore possibilities and investments with a strategic focus—will be leaders in a brand-new competitive landscape.
For more insight, click through to Accenture’s 2019 Technology Vision for Insurance.